Transkranielle Gleichstromstimulation (tDCS), schmerzfrei und nachhaltig
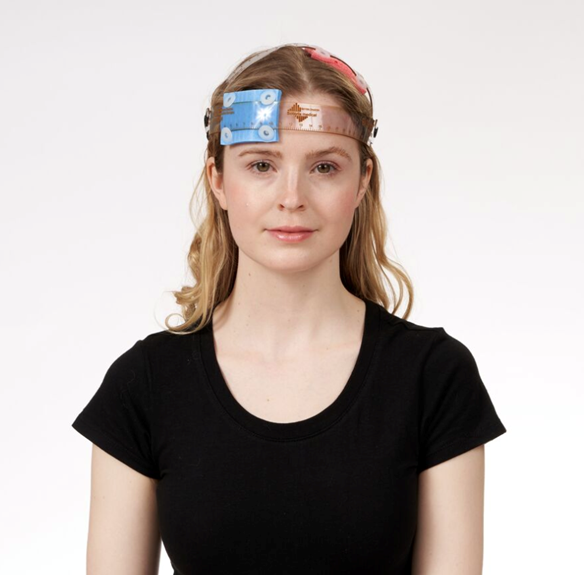

Was ist tDCS?
tDCS ist eine nichtinvasive neurobiologisch basierte Therapieform, bei der über zwei an den Kopf angelegte Schwammelektroden ein sehr feiner, schwacher Strom über das symptomrelevante Hirnareal geleitet und die Erregbarkeit dieses Areals verändert wird: beispielsweise Erhöhung der Erregbarkeit im Bereich des elektrisch minderaktiven Depressionsareals bei Depressionen oder Herabsetzung der Erregbarkeit im Bereich des Schmerzgedächtnisses bei chronischen Schmerzen. Beachten Sie bitte auch die Informationen über die Wirkverstärkung bei Kombination mit Ketamin auf der Startseite.
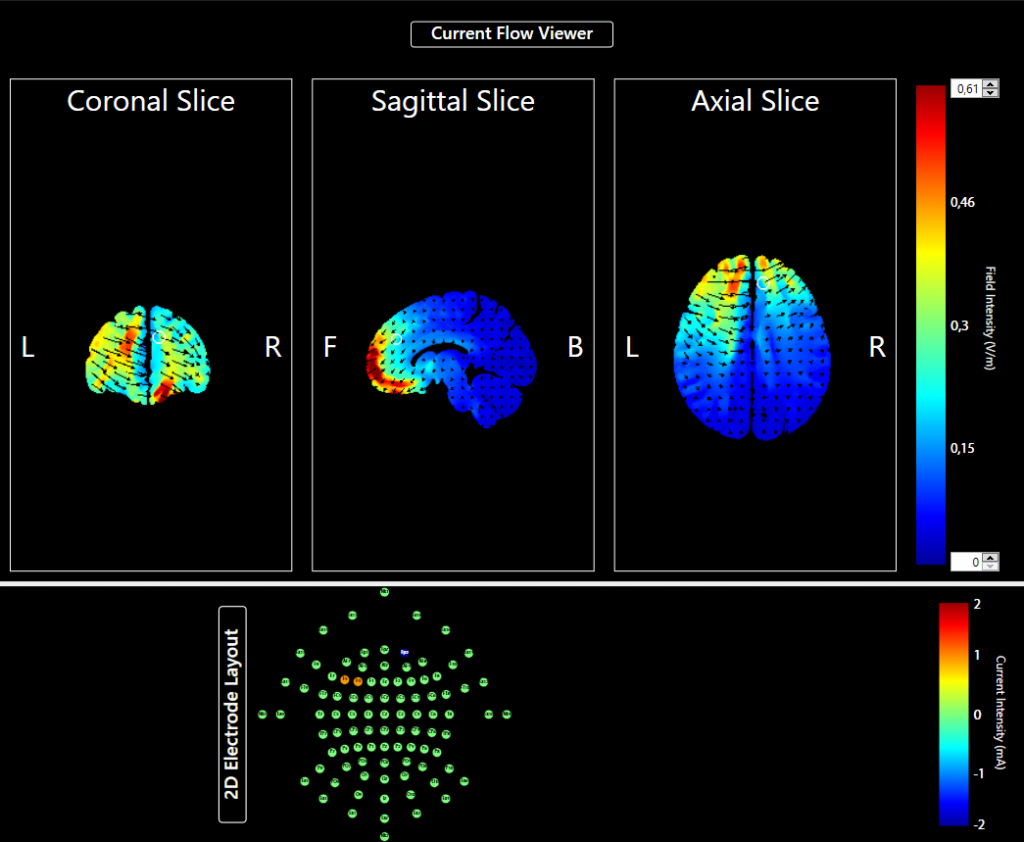
Es ist aber nicht die tDCS, sondern das durchgeführte Protokoll, das über die Wirksamkeit entscheidet. Deshalb setzen wir Soterix-Neurotargeting-Software ein, ein aus der Hirnforschung stammendes Instrumentarium zur Therapieoptimierung. Wir schätzen uns glücklich, darauf zurückgreifen zu können. Letztlich bestimmen Größe und Position der Elektroden, Dauer, Intensität (mA) und Richtung (Polarität) des verwendeten Stroms über den Erfolg. In Abhängigkeit davon finden sich in der wissenschaftlichen Fachliteratur reproduzierbare positive Effekte auf bestimmte psychiatrische und Schmerzerkrankungen.
Die im Bereich der Universitätsmedizin angesiedelte Therapie ist ausgesprochen schonend, sehr gut wissenschaftlich untersucht und die Ergebnisse sind nachhaltig.
Mögliche Nebenwirkungen von tDCS
tDCS ist ausgesprochen schonend, Nebenwirkungen sehr selten, und wenn sie überhaupt auftreten, vorübergehender und harmloser Natur [1]: Nackenschmerzen (20%), lokaler Schmerz oder Brennen an der Kopfhaut (10%), Kribbeln 40%, Hautrötung unter der Elektrode (10%), Müdigkeit (60%), Konzentrationsstörungen (10%).
- Simis, M., et al., Motor cortex-induced plasticity by noninvasive brain stimulation: a comparison between transcranial direct current stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuroreport, 2013. 24(17): p. 973-5.
Gegenanzeigen tDCS
- nach Schädel-Hirn-Trauma
- nach chirurgischen Eingriffen am Gehirn
- mit elektronischen Implantaten
- nach oder während schweren körperlichen Erkrankungen (z.B. Krebs)
- mit bestimmten psychischen Erkrankungen
- mit bestimmten neurologischen Erkrankungen (z.B. Epilepsie)
- psychotische Symptome oder Suizidalität
- Suchterkrankungen
- Schwangerschaft
- Metallimplantate in Kopf- oder Halsbereich
- infektiöse Hauterkrankungen
Hier können Sie eine Aufklärungspräsentation anschauen:

Publikationen
Depression
- Trial of Electrical Direct-Current Therapy versus Escitalopram for Depression. Brunoni A.R., Moffa A.H., Sampaio-Junior B., Borrione L., Moreno M.L., Fernandes R.A., Veronezi B.P., Nogueira B.S., Aparicio L.V.M., Razza L.B., Chamorro R., Tort L.C., Fraguas R., Lotufo P.A., Gattaz W.F., Fregni F., Benseñor I.M.; ELECT-TDCS Investigators. (2017)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of post-stroke depression: results from a randomised, sham-controlled, double-blinded trial. Valiengo L.C., Goulart A.C., de Oliveira J.F., Benseñor I.M., Lotufo P.A., Brunoni A.R. (2017)
- Concurrent cognitive control training augments the antidepressant efficacy of tDCS: a pilot study. Segrave R.A., Arnold S., Hoy K., Fitzgerald P.B. (2014)
- The sertraline vs. electrical current therapy for treating depression clinical study: results from a factorial, randomized, controlled trial. Brunoni, A.R, Valiengo L., Baccaro A., Zanao T.A., de Oliveira J.F., Goulart A., Boggio P.S., Lotufo P.A., Bensenor I.M., Fregni,F. (2013)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation for depression: 3-week, randomized, sham-controlled trial. Loo C.K., Alonzo A., Martin D., Mitchell P.B., Galvez V., Sachdev P. (2012)
- A randomized, double-blind clinical trial on the efficacy of cortical direct current stimulation for the treatment of major depression. Boggio P.S., Rigonatti S.P., Riberiro R.B., Myczkowski M.L., Nitsche M.A., Pascual-Leone A., Fregni F. (2008)
Fibromyalgie
- Transcranial direct current stimulation in the neuromodulation of pain in fibromyalgia: A case study. DalĺAgnol L., Pascoal-Faria P., Barros Cecílio S., Corrêa FI. (2015)
- Clinically Effective Treatment of Fibromyalgia Pain With High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: Phase II Open-Label Dose Optimization. Castillo-Saavedra L., Gebodh N., Bikson M., Diaz-Cruz C., Brandao R., Coutinho L., Truong D., Datta A., Shani-Hershkovich R., Weiss M., Laufer I., Reches A., Peremen Z., Geva A., Parra L.C., Fregni F. (2015)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation as a treatment for patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Fagerlund A.J., Hansen O.A., Aslaksen P.M. (2015)
- Focal modulation of the primary motor cortex in fibromyalgia using 4×1-ring high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS): immediate and delayed analgesic effects of cathodal and anodal stimulation. Villamar M.F., Wivatvongvana P., Patumanond J., Bikson M., Truong D.Q., Datta A., Fregni F. (2013)
- Non-invasive brain stimulation approaches to fibromyalgia pain. Short B., Borckardt J.J., George M., Beam W., Reeves S.T. (2009)
- Efficacy of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for the treatment of fibromyalgia: results of a randomized, sham-controlled longitudinal clinical trial. Valle A., Roizenblatt S., Botte S., Zaghi S., Riberto M., Tufik S., Boggio P.S., Fregni F. (2009)
- Site-specific effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on sleep and pain in fibromyalgia: a randomized, sham-controlled study. Roizenblatt S., Fregni F., Gimenez R., Wetzel T., Rigonatti S.P., Tufik S., Boggio P.S., Valle A.C. (2007)
- A randomized, sham-controlled, proof of principle study of transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of pain in fibromyalgia. Fregni F., Gimenes R., Valle A.C., Ferreira M.J., Rocha R.R., Natalle L., Bravo R., Rigonatti S.P., Freedman S.D., Nitsche M.A., Pascual-Leone A., Boggio P.S. (2006)
Migräne
- State-of-art neuroanatomical target analysis of high-definition and conventional tDCS montages used for migraine and pain control. DaSilva A.F., Truong D.Q., DosSantos M.F., Toback R.L., Datta A., Bikson M. (2015)
- Prophylactic treatment in menstrual migraine: A proof-of-concept study. Wickmann F., Stephani C., Czesnik D., Klinker F., Timäus C., Chaieb L., Paulus W., Antal A. (2015)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation in the prophylactic treatment of migraine based on interictal visual cortex excitability abnormalities: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Rocha S., Melo L., Boudoux C., Foerster Á., Araújo D., Monte-Silva K. (2014)
- Clinical effectiveness of primary and secondary headache treatment by transcranial direct current stimulation. Pinchuk D., Pinchuk O., Sirbiladze K., Shugar O. (2013)
- tDCS-induced analgesia and electrical fields in pain-related neural networks in chronic migraine. Dasilva A.F., Mendonca M.E., Zaghi S., Lopes M., Dossantos M.F., Spierings E.L., Bajwa Z., Datta A., Bikson M., Fregni F. (2012)
- Migraine prophylaxis by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation, a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Auvichayapat P., Janyacharoen T., Rotenberg A., Tiamkao S., Krisanaprakornkit T., Sinawat S., Punjaruk W., Thinkhamrop B., Auvichayapat N. (2012)
Andere Schmerzen
- Reduction of chronic abdominal pain in patients with inflammatory bowel disease via transcranial direct current stimulation: a randomized controlled trial. Volz M.S., Farmer A., Siegmund B. (2015)
- Pain reduction associated with improved functional interhemispheric balance following transcranial direct current stimulation for post-stroke central pain: A case study. Morishita T., Hyakutake K., Saita K., Takahara M., Shiota E., Inoue T. (2015)
- Effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation for the management of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis. Mehta S., McIntyre A., Guy S., Teasell R.W., Loh E. (2015)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation and exercises for treatment of chronic temporomandibular disorders: a blind randomised-controlled trial. Oliveira L.B., Lopes T.S., Soares C., Maluf R., Goes B.T., Sá K.N., Baptista A.F. (2015)
- Analgesic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on central post-stroke pain. Bae S.H., Kim G.D., Kim K.Y. (2014)
- Randomized, sham controlled trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Kim Y.J., Ku J., Kim H.J., Im D.J., Lee H.S., Han K.A., Kang Y.J. (2013)
- Postoperative analgesic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation in lumbar spine surgery: a randomized control trial. Dubois P.E., Ossemann M., de Fays K., De Bue P., Gourdin M., Jamart J., Vandermeeren Y. (2013)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) reduces postsurgical opioid consumption in total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Borckardt J.J., Reeves S.T., Robinson S.M., May J.T., Epperson T.I., Gunselman R.J., Schutte H.D., Demos H.A., Madan A., Fredrich S., George M.S. (2013)
- Effects of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on chronic neuropathic pain in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mori F., Codecà C., Kusayanagi H., Monteleone F., Buttari F., Fiore S., Bernardi G., Koch G., Centonze D. (2009)
- A sham-controlled, phase II trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of central pain in traumatic spinal cord injury. Fregni F., Boggio P.S., Lima M.C., Ferreira M.J., Wagner T., Rigonatti S.P., Castro A.W., Souza D.R., Riberto M., Freedman S.D., Nitsche M.A., Pascual-Leone A. (2006)
